Before we dive into the specifics of QGIS data analysis, it is important to understand the basics of GIS and spatial data. GIS stands for Geographic Information System, which is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyse, and display spatial or geographic data. Spatial data refers to any data that has a location component, such as a latitude and longitude or an address. Examples of spatial data include maps, satellite images, and point data representing locations of events or objects.
QGIS is an open-source GIS software that provides a wide range of data analysis and visualization tools. Some of the basic data analysis tools available in QGIS include:
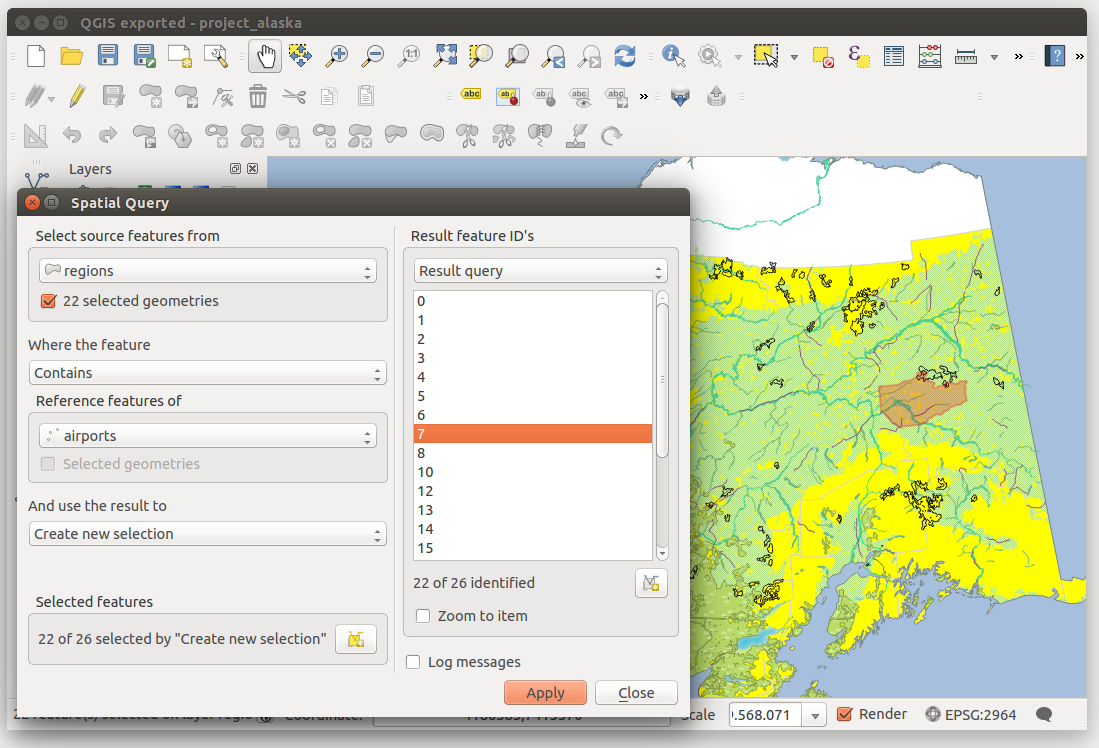
Spatial queries
Vector analysis
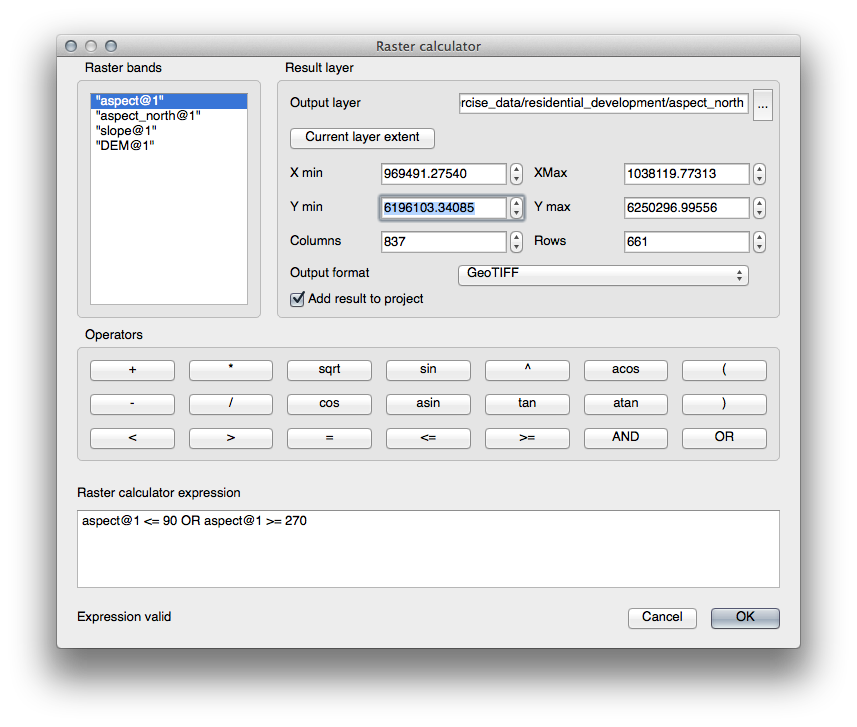
Raster analysis
In addition to these data analysis tools, QGIS also provides a vast array of plugins that can extend its capabilities. Some useful QGIS plugins for data analysis include:
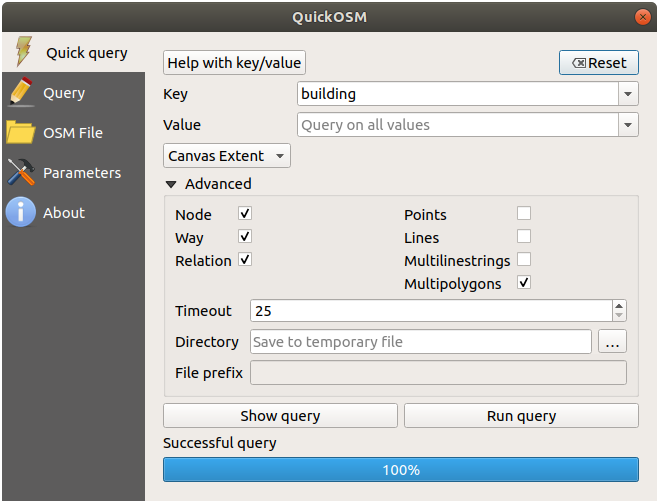
QuickOSM
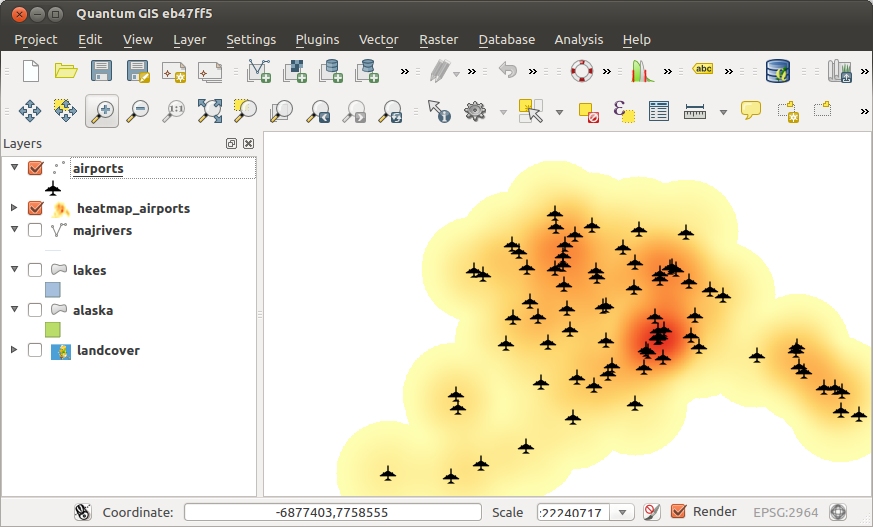
Heatmap
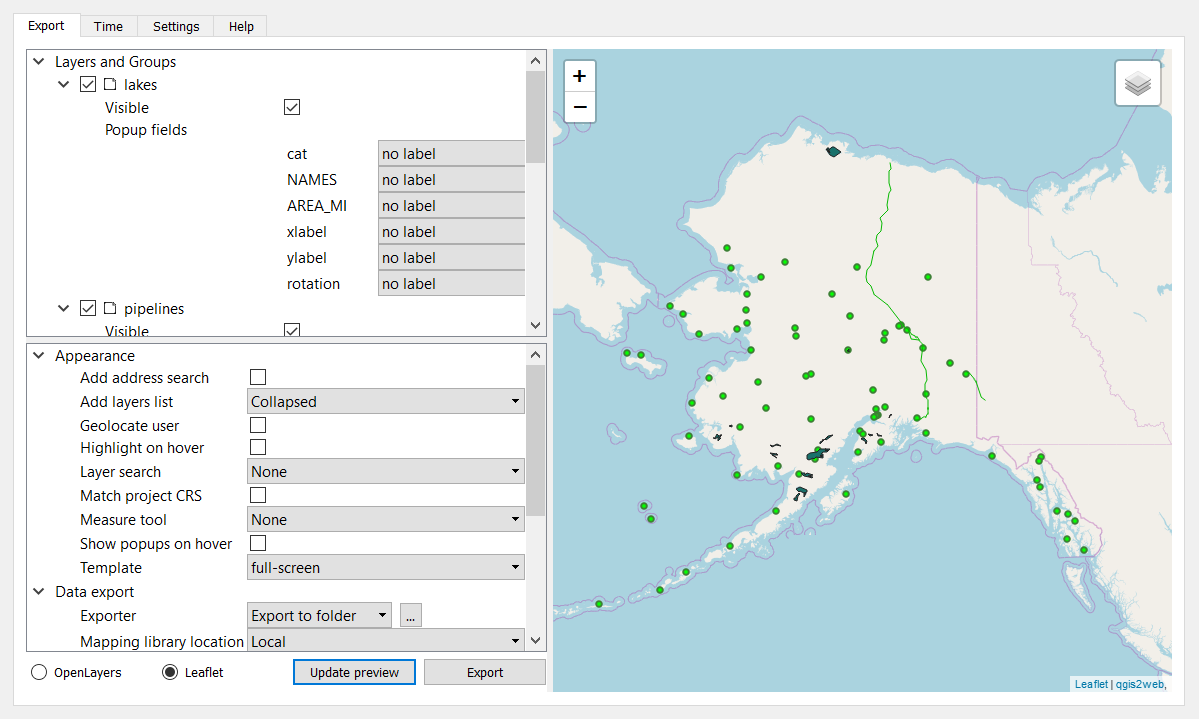
QGIS2Web
In conclusion, QGIS provides a powerful set of tools for data analysis and visualization. As a new user, it might take some time to master these tools, but with practice and guidance, you can easily unlock the full potential of QGIS for your GIS projects.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed